Ionizing Radiation Definition Math
When this process occurs highly reactive free radicals are formed by the creation of unpaired electrons.
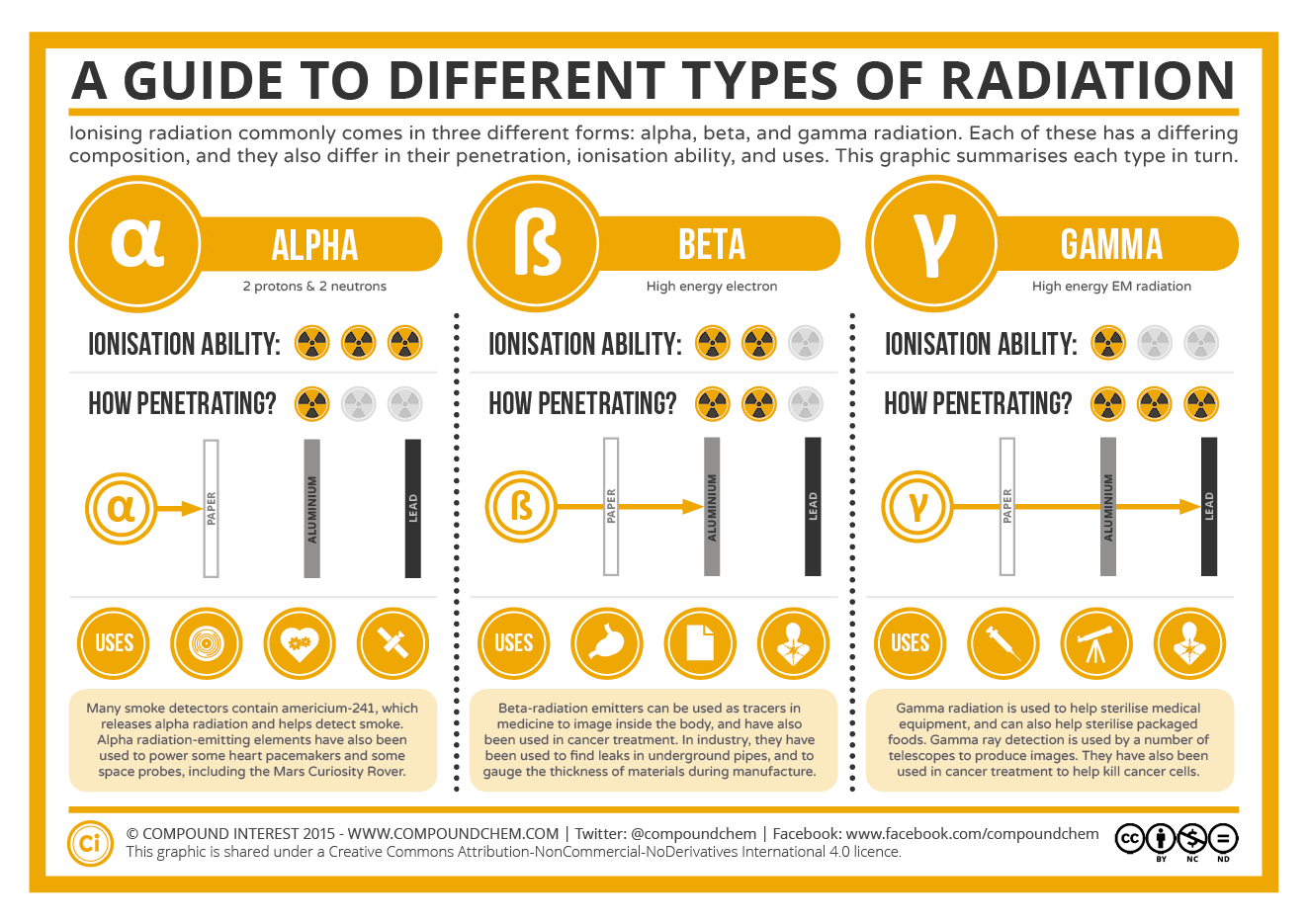
Ionizing radiation definition math. Ionizing radiation is an expensive form of energy whether the radiation source is 60 co or an accelerator and generally at least one of the following criteria are fulfilled in the established radiation processes. Ionizing radiation is radiation with great energy so that during an interaction with the atom it can remove tightly bound electrons from the orbit of an atom causing the atom to be changed from their neutral state. 1 loss of viability 2 alterations in biophysical structure 3 loss of functional capabilities 4 biochemical changes and 5 evidence of injury to subcellular components. Ionizing radiation n rays of rapidly moving subatomic particles x reys or gamma rays sufficiently energetic to cause ionization when absorbed by matter.
Such radiation is emitted by radioactive elements or may be generated by highly energetic physical processes as in stars. Direct and indirect ionizing radiation. Such cells can be examined for. Ionizing radiation occurs in two forms waves or particles.
This leads to highly reactive atomic and molecular species that can interact with other atoms and molecules. Photons and particles with sufficient energy have the ability to liberate orbital electrons from atoms and their corresponding molecules. Ionizing radiation ionising radiation is radiation traveling as a particle or electromagnetic wave that carries sufficient energy to detach electrons from atoms or molecules thereby ionizing an atom or a molecule. Ionizing radiation flow of energy in the form of atomic and subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that is capable of freeing electrons from an atom causing the atom to become charged or ionized.























