Fungi Chitin Math
Fungal chitin is a component of the structural membranes and cell walls of mycelia stalks and spores.
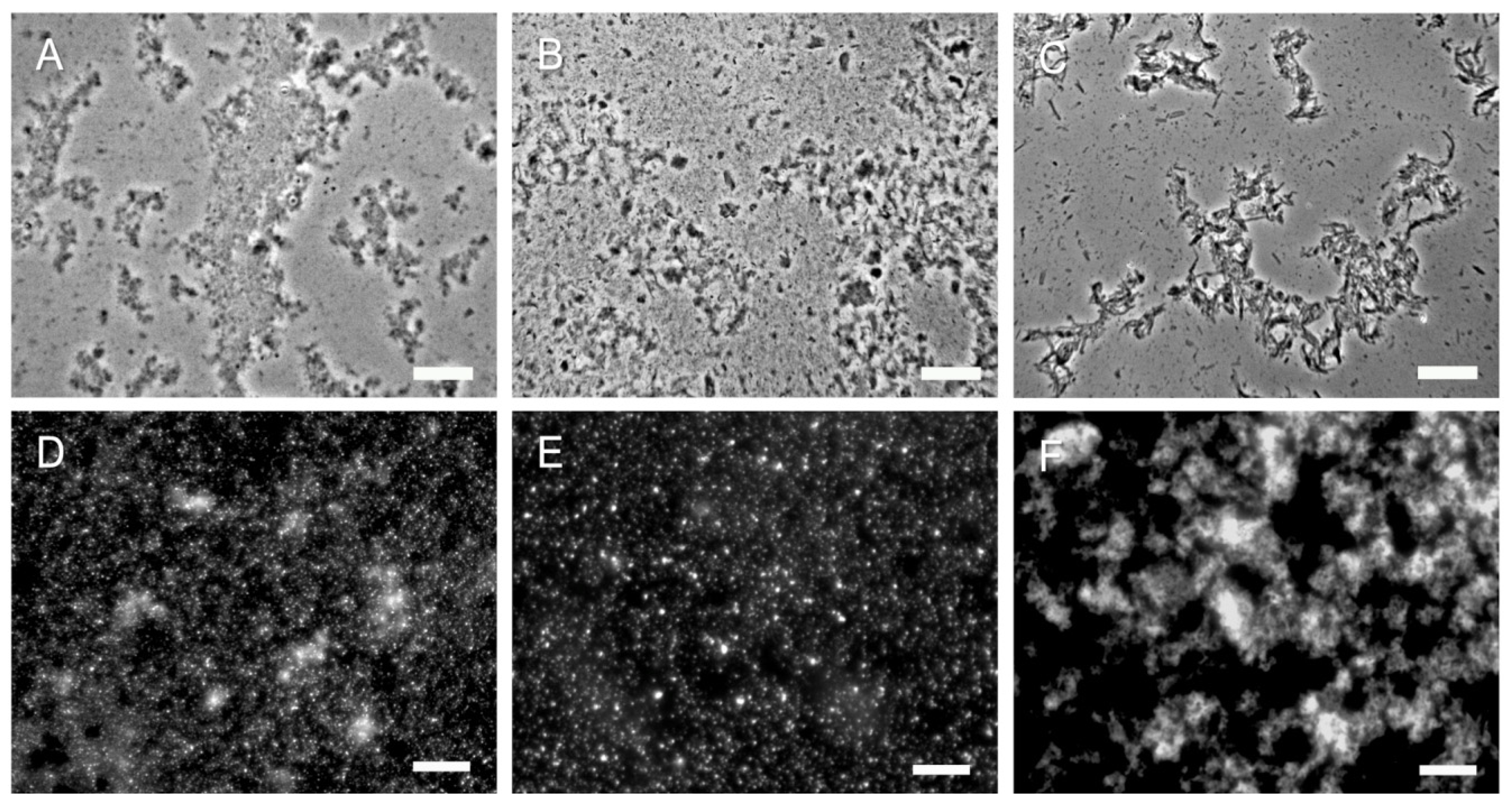
Fungi chitin math. This forms a rigid cell wall between cells which help the organisms retain their shape. Chitin function is described below. Recent research has suggested that localization of chitin synthase. Chitin with the chemical formula c 8 h 13 o 5 n n is considered as a complex carbohydrate whose structure resembles that of cellulose with one hydroxyl group on each monomer replaced with an acetyl amine group.
A major constituent of fungal cell walls is chitin a homopolymer of n acetylglucosamine units. Solution for fungi describe the body structure of fungi such as cell walls made of chitin mycelia hyphae and haustoria know the domain and supergroup of. Multiple signaling pathways have been implicated in chitin synthase regulation at both transcriptional and post transcriptional levels. Fungal chitin synthesis is a complex and highly regulated process.
Fungal cell walls play an important role in conferring mechanic stability during cell division and polar growth. In fungi chitin is used to create a cell wall. However it is a dominant substance. Chitin is widely distributed in many classes of fungi including ascomycetes basidiomycetes and phycomycetes.
Whereas transcription appears to be affected by a variety of external and internal factors these changes in mrna levels do not necessarily correlate with changes in chitin synthase activity or cell wall chitin content. Much like cellulose in plants the chitin is deposited extracellularly with proteins and other molecules. Additionally in phytopathogenic fungi the cell wall is the first structure that gets into intimate contact with the host plant.











/penicillium-notatum-fungus-in-culture-680790505-58b7295d3df78c060ef40413.jpg)












